Page 1 of 2
Earlier this week, the IRS issued Notice 2019-63, which extends both: (1) the filing deadline for Forms 1095-C and 1095-B; and (2) the good-faith reporting relief. But this year, there’s more. In limited circumstances, the IRS will not penalize entities for the failure to furnish information to individuals using Form 1095-B, and in some cases, Form 1095-C (see discussion of Section 6055 Relief below).
Notice 2019-63 extends the due date for reporting entities to furnish 2019 Forms 1095-C and 1095-B to individuals from January 31, 2020 to March 2, 2020. These forms must also be filed with the IRS (along with the applicable transmittal statement) by February 28, 2020 (if filed on paper) or March 31, 2020 (if filed electronically). Reporting entities may, however, request individual extensions to file these forms with the IRS.
The IRS may impose penalties of up to $270 per form for failing to furnish an accurate Form 1095-C or 1095-B to an individual and $270 per form for failing to file an accurate Form 1095-C or 1095-B with the IRS. As in prior years, the IRS indicated in Notice 2019-63 that it would not impose these penalties for incomplete or inaccurate forms for the 2019 calendar year (due in 2020), if the reporting entity can show that it “made good-faith efforts to comply with the information-reporting requirements.” This good-faith reporting relief does not apply to forms that were untimely furnished to individuals or filed with the IRS.
Under Section 6055 of the Internal Revenue Code (the “Code”), providers of minimum essential coverage must furnish certain information to “responsible individuals” about enrollment in the minimum essential coverage during the previous calendar year. The purpose of this reporting requirement is to assist the IRS enforce compliance with the “individual mandate” penalty under the ACA.
Under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017, the individual mandate penalty was not repealed, but the penalty amount was reduced to zero. This makes reporting under Section 6055 of the Code irrelevant. As a result, Notice 2019-63 provides limited relief from the reporting requirements under Section 6055 of the Code.
Here is a brief summary of the Section 6055 reporting requirements:
Notice 2019-63 provides relief with respect to Forms 1095-B and limited relief with respect to Forms 1095-C. For insurers and small self-funded employers, the entity must still prepare and file the Forms 1095-B with the IRS. However, these entities are not required to furnish individuals with a copy of the Form 1095-B as long as the entity satisfies both of the following requirements:
Notice 2019-63 generally does not extend this relief to large self-funded employers, except for Forms 1095-C that are prepared on behalf of individuals who are not full-time employees for the entire 2019 calendar year. A large employer sponsor of a self-funded plan may file a Form 1095-C on behalf of an individual who was enrolled in the self-funded plan during the 2019 calendar year, but was not a full-time employee during any month of the calendar year. (For these individuals, the “all 12 months” column of line 14 is completed using the code “1G.”) Examples of where this relief may extend to Forms 1095-C are: (1) former employees who terminated employment before 2019 but were enrolled in the self-funded plan under COBRA or retiree coverage; and (2) employees who were part-time during all of 2019, but were enrolled in the self-funded plan because the plan sponsor extended eligibility for the self-funded plan to part-time employees.
While the filing deadline extension and the extension of the good-faith reporting relief is likely welcome news to insurers and employers alike, it’s probably not surprising. And, while the Section 6055 reporting relief is likely surprising, it’s probably only meaningful to insurers.
In a recent statement released by the IRS it advised that it would not accept individual 2017 tax returns that did not indicate whether the individual had health coverage, had an exemption from the individual mandate, or will make a shared responsibility payment under the individual mandate. Therefore, for the first time, an individual must complete line 61 (as shown in previous iterations) of the Form 1040 when filing his/her tax return. This article explains what the new IRS position means for the future of ACA compliance from an employer’s perspective.
First, it will be critical (more so this year than in year’s past) that an employer furnish its requisite employees the Form 1095-C by the January 31, 2018 deadline. In previous years, this deadline was extended (to March 2, 2017 last year). However, with the IRS now requiring the ACA information to be furnished by individual tax day, April 17, 2018, employers will almost certainly have to furnish the Form 1095-C to employees by the January 31, 2018 deadline. This is a tight deadline and will require employers to be on top of their data as the 2017 calendar year comes to a close.
An employee who is enrolled in a self-insured plan will need the information furnished in part III of the Form 1095-C to complete line 61 on his/her tax return. It is reasonable to assume that an employee is more likely to inquire as to the whereabouts of the Affordable Care Act information necessary to complete his/her 2017 tax return. Therefore, the possibility of word getting back to the IRS that an employer is not furnishing the Form 1095-C statements to employees is also likely greater in 2017 compared to past years. Remember, an employer can be penalized $260 if it fails to furnish a Form 1095-C that is accurate by January 31, 2018 to the requisite employees. This penalty is capped at $3,218,500. The $260 per Form penalty and the cap amount can be increased if there is intentional disregard for the filing requirements.
The IRS statement continues the IRS’ trend of being more strenuous with ACA requirements. Many employers have received correspondence from the IRS about missing Forms 1094-C and 1095-C for certain EINs. Frequently, this has been caused by the employer incorrectly filing one Form 1094-C for the aggregated ALE group as opposed to a Form 1094-C for each Applicable Large Employer member (ALE member). While the IRS’ latest statement does not ensure that enforcement of the employer mandate (the section 4980H penalties) is coming soon, one could infer that the IRS will soon be sending out penalty notices with respect to the employer mandate.
With the actions taken by the IRS in 2017, all employers need to be taking the reporting of the Forms 1094-C and 1095-C seriously. As of the date of this publication, the Form 1095-C must be furnished to an employer’s requisite employees by January 31, 2018.
Yesterday (May 4, 2017) , the House of Representatives narrowly passed the American Health Care Act of 2017 (AHCA), which contains major parts that would repeal and replace the Affordable Care Act (commonly referred to as Obamacare or ACA). The next obstacle the bill faces is making it through the Senate, which proves to be a formidable challenge.
The nonpartisan Congressional Budget Office has not had time yet to analyze the current version of the bill, but this is expected next week. The bill must now pass the Senate and could get pushed back to the House if it sees changes in the upper chamber.
In the meantime, here are some highlights we know about the bill based on how it is written today and how it would work:
We will continue to keep you up to date on the bill as it progress through legislation.
On Feb. 15, the IRS announced on its ACA Information Center for Tax Professionals webpage that it would not reject taxpayers’ 2016 income tax returns that are missing health coverage information.
This information is supposed to be included on line 61 of the Form 1040 and line 11 of the Form 1040EZ to demonstrate compliance during the year with the Affordable Care Act’s (ACA’s) mandate that individuals have health insurance that meets ACA standards, or else pay a penalty.
Two crucial points regarding the IRS announcement should be stressed:
The IRS indicated that it will accept tax returns lacking this information in light of President Donald Trump’s executive order directing agencies to minimize the ACA’s regulatory burden. While the requirement to have ACA-compliant coverage or pay a tax penalty has been in place since 2014, starting this year the IRS was to have begun automatically flagging and rejecting tax returns missing that information.
“This action by the IRS doesn’t mean it won’t enforce the individual mandate,” said Lisa Carlson, senior Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA) attorney at Lockton Compliance Services in Chicago. “This action simply means the IRS won’t reject a taxpayer’s return outright if the taxpayer doesn’t answer the health coverage question. The IRS reserves the right to follow up with a taxpayer, at a future date, regarding his or her compliance with the individual mandate, if the person’s tax return doesn’t provide information about his or her health insurance coverage during 2016.”
For those individuals who previously filed without providing health insurance information or who indicated that they did not carry coverage as was required, “whether the IRS will assess penalties depends on the retroactive nature of [a possible future] repeal of the individual mandate or its penalties,” Carlson said.
While the IRS announcement does not suggest that the agency won’t be strictly enforcing the individual mandate tax penalty, “we just don’t know” what enforcement actions the agency might take, said Garrett Fenton, an attorney with Miller & Chevalier in Washington, D.C., whose practice focuses on employee benefits, tax and executive compensation.
While it’s unclear how strenuous IRS enforcement actions might be, “the individual mandate and its related tax penalties are certainly still on the books, and it would require an act of Congress to change that,” Fenton noted. If tax filers leave unchecked the box indicating that they have ACA-compliant coverage, “the IRS may come back and ask them follow-up questions, and they still may get audited and potentially owe the tax penalty.”
The ACA is still the law of the land and prudent employers will want to continue to comply with the ACA, including the play-or-pay mandate and reporting requirements, including furnishing Forms 1095-C to employees and making all required filings with the IRS, until formal guidance relieves them of those compliance obligations.
Despite the IRS announcement, employers are still required to file their ACA reporting forms and those forms will be rejected if they do not contain the requisite information. Because the President has indicated that we may not see a repeal until 2018, employers will still be required to operate their health plans in an ACA-compliant manner until notified otherwise.
In the context of the employer mandate, waiver of penalties seems unlikely because these penalties are written into law and are a significant source of revenue for the federal government.
The bottom line: Those who are responsible for issuing and filing 1094s and 1095s on behalf of their organizations should continue to comply with all relevant laws, regulations, reporting requirements and filing specifications during the repeal-and-replace process.
The IRS issued Notice 2016-70 in November 2016, giving employers subject to the ACA’s 2016 information-reporting requirements up to an additional 30 days to deliver these forms to employees. The notice affected upcoming deadlines for ACA information reporting as follows:
The Treasury Department and the IRS determined that a substantial number of employers and other insurance providers needed additional time “to gather and analyze the information [necessary to] prepare the 2016 Forms 1095-C and 1095-B to be furnished to individuals,” Notice 2016-70 stated. This extension applies for tax year 2016 only and does not require the submission of any request or other documentation to the IRS.
Although the date for filing with the IRS was not extended, employers can obtain a 30-day extension by submitting Form 8809 (Application for Extension of Time to File Information Returns) by the due date for the ACA information returns.
Note: For small businesses with fewer than 50 full-time equivalent employees that provide employees with an ACA-compliant group plan, the rules are a bit different. If fully insured, the insurance company that provides coverage is required to send enrollees a copy of Form 1095-B and to submit Forms 1995-B (along with transmittal Form 1094-B) to the IRS in order to report minimum essential coverage.
If a small company is self-insured and provides group coverage, it must also provide employees and the IRS with Form 1095-B. But small business that offer insurance are not required to send Form 1095-Cs to employees or to the IRS.
Small business that do not provide group coverage are not subject to ACA reporting.
While Congress considers options to repeal and replace the ACA, businesses should prepare to comply with the current employer mandate through 2018. Businesses should pay close attention to decisions over the next few weeks, but be prepared to stay patient because significant details on employer obligations are unlikely to take shape for some time.
In July 2015, President Obama signed into law the Trade Preferences Extension Act of 2015. Included in the bill was an important provision that affects welfare and retirement benefit plans. The Act sizably increases filing penalties for information return and statement failures under the Internal Revenue Code, effective for filings after December 31,2015. Employers now face significantly larger penalties for failing to correctly file and furnish the ACA forms 1094 and 1095 (shared responsibility reporting requirements) as well as Forms W-2 and 1099-R.
Background
Sections 6721 and 6722 of the IRC impose penalties associated with failures to file- or to file correct- information returns and statements. Section 6721 applies to the returns required to be filed with the IRS, and Section 6722 applies to statements required to be provided generally to employees.These penalty provisions apply to the ACA shared responsibility reporting Forms 1094-B, 1094-C, 1095-B, and 1095-C (Sections 6055 & 6056) failures as well as other information returns and statement failures, like those on Forms W-2 and 1099.
For ACA:
The Sections 6055 & 6056 reporting requirements are effective for medical coverage provided on or after January 1, 2015, with the first information returns to be filed with the IRS by February 29, 2016 (or March 31,2016 if filing electronically) and provided to individuals by February 1, 2016.
Increase in Penalties
The Trade Preferences Extension Act of 2015 (Act) contains several tax provisions in addition to the trade measures that were the focus of the bill. Provided as a revenue offset provision, the law significantly increases the penalty amounts under Sections 6721 and 6722. A failure includes failing to file or furnish information returns or statements by the due date, failing to provide all required information, as well as failing to provide correct information.
The law increases the penalty for:
Other penalty increase also apply, including those associated with timely filing a corrected return. Penalties could also provide a one-two punch under the ACA for employers and other responsible entities. For example, under Sec 6056, applicable large employers (ALE) must file information returns to the IRS (the 1094-B and 1094-C) as well as furnish statements to employees (the 1095-B and 1095-C). So incorrect information shared on those forms could result in a double penalty- one associated with the information return to the IRS and the other associated with individual statements to employees.
Final regulations on the ACA reporting requirements provide short-term relief from these penalties. For reports files in 2016 (for 2015 calendar year info), the IRS will not impose penalties on ALE members that can show they made a “good-faith effort” to comply with the information reporting requirements. Specifically, relief is provided for incorrect or incomplete info reported on the return or statement, including Social Security numbers, but not for failing to file timely.
Beginning January 1, 2015, employers have new reporting obligations for health plan coverage, to allow the government to administer the “pay or play” penalties to be assessed against employers that do not offer compliant coverage to their full-time employees.
Even though the penalties only apply if there are 100 or more employees for 2015, employers with 50 or more full-time equivalent employees are required to report for 2015. Also, note this reporting is required even if the employer does not maintain any health plan.
Employers that provide self-funded group health coverage also have reporting obligations, to allow the government to administer the “individual mandate” which results in a tax on individuals who do not maintain health coverage.
These reporting obligations will be difficult for most employers to implement. Penalties for non-compliance are high, so employers need to begin now with developing a plan on how they will track and file the required information.
Pay or Play Reporting. Applicable large employers (ALEs) must report health coverage offered to employees for each month of 2015 in an annual information return due early in 2016. ALEs are employers with 50 or more full-time equivalent (FTE) employees. Employees who average 30 hours are counted as one, and those who average less than 30 hours are combined into an equivalent number of 30 hour employees to determine if there are 50 or more FTE employees. All employees of controlled group, or 80% commonly owned employers, are also combined to determine if the 50 FTE threshold is met.
Individual Mandate Reporting. Self-funded employers, including both ALEs and small employers that are not ALEs, must report each individual covered for each month of the calendar year. For fully-insured coverage, the insurance carrier must report individual month by month coverage. The individual mandate reporting is due early in 2016 for each month of 2015.
Which Form? ALE employers have one set of forms to report both the pay or play and the individual mandate information – Forms 1094C and 1095C. Insurers and self-insured employers that are not ALEs use Forms 1094B and 1095B to report the individual mandate information. Information about employee and individual coverage provided on these forms must also be reported by the employer to its employees as well as to COBRA and retiree participants. Forms 1095B and 1095C can be used to provide this information, or employers can provide the information in a different format.
The following chart summaries which returns are filed by employers:
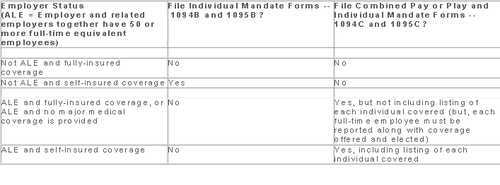
Who Reports? While ALE status is determined on a controlled group basis, each ALE must file separate reports. Employers will need to provide insurance carriers, and third party administrators who process claims for self-funded coverage (if they will assist the employer with reporting), accurate data on the employer for whom each covered employee works. If an employee works for more than one ALE in a controlled group, the employer for whom the highest number of hours is worked does the reporting for that employee.
Due Date for Filing. The due date of the forms matches the due dates of Forms W-2, and employers may provide the required employee statements along with the W-2. Employee reporting is due January 31st and reporting to the IRS is due each February 28th, although the date is extended until March 31st if the forms are filed electronically. If the employer files 250 or more returns, the returns must be filed electronically. Reporting to employees can only be made electronically if the employee has specifically consented to receiving these reports electronically.
Penalties. Failure to file penalties can total $200 per individual for whom information must be reported, subject to a maximum of $3 million per year. Penalties will not be assessed for employers who make a good faith effort to file correct returns for 2015.
What Information is Required? For the pay or play reporting, each ALE must file a Form 1094C reporting the number of its full-time employees (averaging 30 hours) and total employees for each calendar month, whether the ALE is in a “aggregated” (controlled) group, a listing of the name and EIN of the top 30 other entities in the controlled group (ranked by number of full-time employees), and any special transition rules being used for pay or play penalties. ALE’s must also file a 1095C for each employee who was a full-time employee during any calendar month of the year. The 1095C includes the employee’s name, address and SSN, and month by month reporting of whether coverage was offered to the employee, spouse and dependents, the lowest premium for employee only coverage, and identification of the safe-harbor used to determine affordability. This information is used to determine pay or play penalty taxes and to verify the individuals’ eligibility for subsidies toward coverage costs on the Federal and state exchanges.
If the ALE provides self-funded coverage, the ALE must also report on the 1095C the name and SSN of each individual provided coverage for each calendar month. If an employer is not an ALE, but is self-funded, the name and SSN of each covered individual is reported on the 1095B and the 1094B is used to transmit the forms 1095B to the IRS.
A chart is available that sets out what data must be reported on each form, to help employers determine what information they need to track. Click here to access the chart.
Next Steps. Employers will need to determine how much help their insurance carrier or TPA can provide with the reporting, and then the employer’s HR, payroll and IT functions will need to work together to be sure the necessary information is being tracked and can be produced for reporting in January 2016.
The Affordable Care Act will require Applicable Large Employers (i.e. large employers subject to the employer mandate) and employers sponsoring self-insured plans to comply with new annual IRS reporting requirements. The first reporting deadline will be February 28, 2016 as to the data employers collect during the 2015 calendar year. The reporting provides the IRS with information it needs to enforce the Individual Mandate (i.e. individuals are penalized for not having health coverage) and the Employer Mandate (i.e. large employers are penalized for not offering health coverage to full-time employees). The IRS will also require employers who offer self-insured plans to report on covered individuals.
Large employers and coverage providers must also provide a written statement to each employee or responsible individual (i.e. one who enrolls one or more individuals) identifying the reported information. The written statement can be a copy of the Form.
The IRS recently released draft Forms 1094-C and 1095-C and draft Forms 1094-B and 1095-B, along with draft instructions for each form.
Which Forms Do I File?
When?
Statements to employees and responsible individuals are due annually by January 31. The first statements are due January 31, 2016.
Forms 1094-B, 1095-B, 1094-C and 1095-C are due annually by February 28 (or by March 31, if filing electronically). The first filing is due by February 28, 2016 (or March 31, 2016, if filing electronically).
Even though the forms are not due until 2016, the annual reporting will be based on data from the prior year. Employers need to plan ahead now to collect data for 2015. Many employers have adopted the Look Back Measurement Method Safe Harbor (“Safe Harbor”) to identify full-time employees under the ACA. The Safe Harbor allows employers to “look back” on the hours of service of its employees during 2014 or another measurement period. There are specific legal restrictions regarding the timing and length of the periods under the Safe Harbor, so employers cannot just pick random dates. Employers also must follow various rules to calculate hours of service under the Safe Harbor. The hours of service during the measurement period (which is likely to include most of 2014) will determine whether a particular employee is full-time under the ACA during the 2015 stability period. The stability period is the time during which the status of the employee, as full-time or non-full-time, is locked in. In 2016, employers must report their employees’ full-time status during the calendar year of 2015. Therefore, even though the IRS forms are not due until 2016, an employee’s hours of service in 2014 will determine how an employer reports that employee during each month of 2015. Employers who have not adopted the Safe Harbor should consider doing so because it allows an employer to average hours of service over a 12-month period to determine the full-time status of an employee. If an employer does not adopt the Safe Harbor, the IRS will require the employer to make a monthly determination, which is likely to increase an employer’s potential exposure to penalties.
What Must the Employer Report?
Form 1095-C
There are three parts to Form 1095-C. An applicable large employer must file one Form 1095-C for each full-time employee. If the applicable large employer sponsors self-insured health plans, it must also file Form 1095-C for any employee who enrolls in coverage regardless of the full-time status of that employee.
Form 1095-C requires the employer to identify the type of health coverage offered to a full-time employee for each calendar month, including whether that coverage offered minimum value and was affordable for that employee. Employers must use a code to identify the type of health coverage offered and applicable transition relief.
Employers that offer self-insured health plans also must report information about each individual enrolled in the self-insured health plan, including any full-time employee, non-full-time employee, employee family members, and others.
Form 1094-C
Applicable large employers use Form 1094-C as a transmittal to report employer summary information and transmit its Forms 1095-C to the IRS. Form 1094-C requires employers to enter the name and contact information of the employer and the total number of Forms 1095-C it submits. It also requires information about whether the employer offered minimum essential coverage under an eligible employer-sponsored plan to at least 95% of its full-time employees and their dependents for the entire calendar year, the number of full-time employees for each month, and the total number of employees (full-time or non-full-time) for each month.
Form 1095-B
Employers offering self-insured coverage use Form 1095-B to report information to the IRS about individuals who are covered by minimum essential coverage and therefore are not liable for the individual shared responsibility payment. These employers must file a Form 1095-B for eachindividual who was covered for any part of the calendar year. The employer must make reasonable efforts to collect social security numbers for covered individuals.
Form 1094-B
Employers who file Form 1095-B will use Form 1094-B as a transmittal form. It asks for the name of the employer, the employer’s EIN, and the name, telephone number, and address of the employer’s contact person.
Failure to Report – What Happens?
The IRS will impose penalties for failure to timely provide correct written statements to employees. The IRS will also impose penalties for failure to timely file a correct return. For the 2016 reporting on 2015 data, the IRS will not impose a penalty for good faith compliance. However, the IRS specified that good faith compliance requires that employers provide the statements and file the returns.
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) imposes significant information reporting responsibilities on employers starting with the 2015 calendar year. One reporting requirement applies to all employer-sponsored health plans, regardless of the size of the employer. A second reporting requirement applies only to large employers, even if the employer does not provide health coverage. The IRS is currently developing new systems for reporting the required information and recently released draft forms, however instructions have yet to be released.
Information returns
The new information reporting systems will be similar to the current Form W-2 reporting systems in that an information return (Form 1095-B or 1095-C) will be prepared for each applicable employee, and these returns will be filed with the IRS using a single transmittal form (Form 1094-B or 1094-C). Electronic filing is required if the employer files at least 250 returns. Employers must file these returns annually by Feb. 28 (March 31 if filed electronically). Therefore, employers will be filing these forms for the 2015 calendar year by Feb. 28 or March 31, 2016 respectively. A copy of the Form 1095, or a substitute statement, must be given to the employee by Jan. 31 and can be provided electronically with the employee’s consent. Employers will be subject to penalties of up to $200 per return for failing to timely file the returns or furnish statements to employees.
The IRS released drafts of the Form 1095-B and Form 1095-C information returns, as well as the Form 1094-B and Form 1094-C transmittal returns, in July 2014 and is expected to provide instructions for the forms in August 2014. According to the IRS, both the forms and the instructions will be finalized later this year.
Health coverage reporting requirement
The health coverage reporting requirement is designed to identify employees and their family members who are enrolled in minimum essential health coverage. Employees who are offered coverage, but decline the coverage, are not reported. The IRS will use this information to determine whether the employees are exempt from the individual mandate penalty due to having health coverage for themselves and their family members.
Insurance companies will prepare Form 1095-B (Health Coverage) and Form 1094-B (Transmittal of Health Coverage Information Returns) for individuals covered by fully-insured employer-sponsored group health plans. Small employers with self-insured health plans will use Form 1095-B and Form 1094-B to report the name, address, and Social Security number (or date of birth) of employees and their family members who have coverage under the self-insured health plan. However, large employers (as defined below) with self-insured health plans will file Forms 1095-C and 1094-C in lieu of Forms 1095-B and 1094-B.
Large employer reporting requirement
“Applicable large employer members (ALE)” are subject to the reporting requirement if they offer an insured or self-insured health plan, or do not offer any group health plan. ALE members are those employers that are either an applicable large employer on their own or are members of a controlled or affiliated service group with an ALE (regardless of the number of employees of the group member). ALEs are those that had, on average, at least 50 full-time employees (including full-time equivalent “FTE” employees) during the preceding calendar year. Full-time employees are those who work, on average, at least 30 hours per week. Employers with fewer than 50 full-time employees and equivalents are not applicable large employers and, thus, are exempt from this health coverage reporting requirement.
As referenced above, an employer’s status as an ALE is determined on a controlled or affiliated service group basis. For example, if Company A and Company B are members of the same controlled group and Company A has 100 employees and Company B has 20 employees, then A and B are both members of an ALE. Consequently, Company A and Company B must each file the information returns.
Each ALE member must file Form 1095-C (Employer-Provided Health Insurance Offer and Coverage) and Form 1094-C (Transmittal of Employer-Provided Health Insurance Offer and Coverage Information Returns) with the IRS for each calendar year. The IRS will use this information to determine whether (1) the employer is subject to the employer mandate penalty, and (2) an employee is eligible for a premium tax credit on insurance purchased through the new health insurance exchange. ALEs with fewer than 100 full-time employees are generally eligible for transition relief from the employer mandate penalty for their 2015 plan year. Nonetheless, these employers are still required to file Forms 1095-C and 1094-C for the 2015 calendar year.
The employer mandate penalty can be imposed on any ALE member that does not offer affordable, minimum value health coverage to all of its full-time employees starting in 2015. Health coverage is affordable if the amount that the employer charges an employee for self-only coverage does not exceed 9.5 percent of the employee’s Form W-2 wages, rate of pay, or the federal poverty level for the year. A health plan provides minimum value if the plan is designed to pay at least 60 percent of the total cost of medical services for a standard population. In the case of a controlled or affiliated service group, the employer mandate penalties apply to each member of the group individually.
ALE members must prepare a Form 1095-C for each employee. The return will report the following information:
An ALE member will file with the IRS one Form 1094-C transmitting all of its Forms 1095-C. The Form 1094-C will report the following information:
As noted above, each ALE member is required to file Forms 1095-C and 1094-C for its own employees, even if it participates in a health plan with other employers (e.g., when the parent company sponsors a plan in which all subsidies participate). Special rules apply to multiemployer plans for collectively-bargained employees.
Action required
In light of the complexity of the new information reporting requirements, it is recommended that employers should begin taking steps now to prepare for the new reporting requirements:
Starting in 2015, the Affordable Care Act (ACA) requires applicable large employers to offer affordable, minimum value health coverage to their full time employees (and dependents) or pay a penalty. The employer penalty rules are also known as the employer mandate or the “pay or play” rules.
Effective in 2014, affordability of health coverage is used to determine whether an individual is:
On July 24, 2014, the IRS released Revenue Procedure 2014-37 to index the ACA’s affordability percentages for 2015.
For plan years beginning in 2015, an applicable large employer’s health coverage will be considered affordable under the pay or play rules if the employee’s requires contribution to the plan does not exceed 9.56 percent of the employee’s household income for the year. The current affordability percentage for 2014 is 9.5 percent.
Applicable large employers can use one of the IRS’ affordability safe harbors to determine whether their health plans will satisfy the 9.56 percent requirement for 2015 plan years, if requirements for the applicable safe harbor are met.
This adjusted affordability percentage will also be used to determine whether an individual is eligible for a premium tax credit for 2015. Individuals who are eligible for employer-sponsored coverage that is affordable and provides minimum value are not eligible for a premium tax credit in the Exchange.
Also, Revenue Procedure 2014-37 adjusts the affordability percentage for the exemption from the individual mandate for individuals who lack access to affordable minimum essential coverage. For plan years beginning in 2015, coverage is unaffordable for purposes of the individual mandate if it exceeds 8.05 percent of household income.
Employer Mandate
The pay or play rules apply only to applicable large employers. An “applicable large employer” is an employer with, on average, at least 50 full-time employees (including full-time equivalents) during the preceding calendar year. Many applicable large employers will be subject to the pay or play rules starting in 2015. However, applicable large employers with fewer than 100 full-time employees may qualify for an additional year, until 2016, to comply with the employer mandate.
Affordability Determination
The affordability of health coverage is a key point in determining whether an applicable large employers will be subject to a penalty.
For 2014, the ACA provides that an employer’s health coverage is considered affordable if the employee’s required contribution to the plan does not exceed 9.5 percent of the employee’s household income for the taxable year. The ACA provides that, for plan year beginning after 2014, the IRS must adjust the affordability percentage to reflect the excess of the rate of premium growth over the rate of income growth for the preceding calendar year.
As noted above, the IRS has adjusted the affordability percentage for plan years beginning in 2015 to 9.56 percent. The affordability text applies only to the portion of the annual premiums for self-only coverage and does not include any additional cost for family coverage. Also, if an employer offers multiple health coverage options, the affordability test applies to the lowest-cost option that also satisfies the minimum value requirement.
Affordability Safe Harbors
Because an employer generally will not know an employee’s household income, the IRS created three affordability safe harbors that employers may use to determine affordability based on information that is available to them.
The affordability safe harbors are all optional. An employer may choose to use one or more of the affordability safe harbors for all its employees or for any reasonable category of employees, provided it does so on a uniform and consistent basis for all employees in a category.
The affordability safe harbors are:
Individual Mandate
Beginning in 2014, the ACA requires most individuals to obtain acceptable health insurance coverage for themselves and their family members or pay a penalty. This rule is often referred to as the “individual mandate”. Individual may be eligible for an exemption from the penalty in certain circumstances.
Under the ACA, individuals who lack access to affordable minimum essential coverage are exempt from the individual mandate. For purposes of this exemption, coverage is considered affordable for an employee in 2014 if the required contribution for the lowest-cost, self-only coverage does not exceed 8 percent of household income. For family members, coverage is considered affordable in 2014 if the required contribution for the lowest-cost family coverage does not exceed 8 percent of household income. This percentage will be adjusted annually after 2014.
For plan years beginning in 2015, the IRS has increased this percentage from 8 percent to 8.05 percent.
Keeping up with changes under the Affordable Care Act (ACA) is a challenge for all employers. Here are the top five issues you should specifically pay attention to as healthcare reform rolls out.
The Employer Mandate
Under the ACA, large employers will be required to provide affordable healthcare insurance that meets minimum value to all full-time employees beginning in 2015. Final regulations issued in February clarify most aspects of how the mandate will be implemented.
The Individual Mandate
Beginning January 1, 2014, all individuals are required to carry qualified health insurance known as “minimum essential coverage” or face penalties when they file taxes in the spring of 2015. In 2014, the penalty for noncompliance will be the greater of $95 per uninsured person or 1% of household income over the filing threshold. This penalty will rise in 2015 and again in 2016.
Wellness Programs
As health insurance costs rise, wellness programs are gaining popularity, however be cautious when designing and maintaining a wellness program because they must conform to new ACA requirements and existing HIPAA nondiscrimination requirements.
Reporting Requirements
Beginning in the spring of 2016, large employers will face a new reporting requirement for the 2015 calendar year. The Form 6056 will ask for information including:
Automatic Enrollment And Nondiscrimination Regulations
Though enforcement of the automatic enrollment and nondiscrimination provisions of the ACA has not started, keep an eye out for regulations that will trigger compliance obligations. Employers with over 100 employees should anticipate that in the next few years, they will be required to automatically enroll all full-time employees for health insurance coverage.
In addition, employers who offer varying levels of coverage or employer-provided subsidies based on classes of employees need to watch for nondiscrimination regulations.
Please contact our office if you have any questions on how Healthcare Reform will affect you or your business.