As we near closer to Thanksgiving, it’s safe to say we are in “late 2017” territory. Last week, the IRS issued new FAQ guidance informing employers that they can expect notice of any potential ACA employer mandate pay or play penalties in late 2017.
What Will the Letter Look Like?
The IRS recently posted a copy of the Letter 226J here: https://www.irs.gov/pub/notices/ltr226j.pdf
Letters Will Look Back to 2015
The ACA employer mandate pay or play rules first took effect in 2015. The IRS Letters 226J at issue will relate only to potential penalties in that first year, and therefore they will be relevant only to employers that were applicable large employers (ALEs) in 2015.
In general, an employer was an ALE in 2015 if it (along with any members in its controlled group) employed an average of at least 50 full-time employees, including full-time equivalent employees, on business days during the preceding calendar year (2014).
Note that a special 2015 transition rule provided that certain “mid-sized” employers between 50 and 100 full-time employees could have reported an exemption from potential pay or play penalties.
What Are the Potential 2015 Penalties?
a) §4980H(a)—The “A Penalty” aka No Coverage Offered
This is the big “sledge hammer” penalty for failure to offer coverage to substantially all full-time employees. In 2015, this standard required an offer of coverage to at least 70% of the ALE’s full-time employees. (For 2016 forward, this standard has been increased to 95%).
The 2015 A Penalty was $173.33/month ($2,080 annualized) multiplied by all full-time employees then reduced by the first 80 full-time employees (reduced by the first 30 full-time employees for 2016 forward). It was triggered by at least one full-time employee who was not offered group coverage enrolling in subsidized coverage on the Exchange.
The reduced 70% threshold for the 2015 penalty should be sufficient for virtually all ALEs in 2015 to avoid the A Penalty, provided they offered a group health plan with eligibility set at 30 hours per week or lower. It would be very unlikely for a surprise A Penalty to arise for 2015.
b) §4980H(b)—The “B Penalty” aka Coverage Not Affordable
This is the much smaller “tack hammer” penalty that will apply where the ALE is not subject to the A Penalty (i.e., the ALE offered coverage to at least 70% of full-time employees in 2015, or 95% thereafter). It applies for each full-time employee who was not offered coverage, offered unaffordable coverage, or offered coverage that did not provide minimum value and was enrolled in subsidized converge on the Exchange.
The 2015 B Penalty was $260/month ($3,120 annualized). Unlike the A Penalty, the B Penalty multiplier is only those full-time employees not offered coverage (or offered unaffordable or non-minimum value coverage) who actually enrolled in the Exchange. The multiple is not all full-time employees.
What Happened to My Section 1411 Certification?
In the vast majority of states, they never came!
In short, the 1411 Certification (typically referred to as Employer Exchange Notices) informs the employer that one or more of their employees have been conditionally approved for subsidies (the Advance Premium Tax Credit) to pay for coverage on the exchange.
One important purpose of the notice is it provides employers with the chance to contemporaneously challenge the employee’s subsidy approval. Near the time of the employee’s subsidy approval, the ALE can show that it made an offer of minimum essential coverage to the full-time employee that was affordable and provided minimum value.
In other words, the notices provide the ALE with the opportunity to prevent the employee from incorrectly receiving the subsidies, and the ALE from ever receiving the Letter 226J from the IRS (because all ACA pay or play penalties are triggered by a full-time employee’s subsidized Exchange enrollment).
CMS admitted in a September 2015 FAQ that they were not able to send the notices for 2015 for federal exchange enrollment (most state exchanges took the same approach), but the potential penalties will nonetheless still apply.
The result is that ALEs will for be receiving their first notice of potential 2015 penalties via IRS Letter 226J in “late 2017.”
How Does the IRS Determine Potential Penalties?
The 2015 ACA reporting via Forms 1094-C and 1095-C (as well as the employee’s subsidized exchange enrollment data for 2015) serve as the primary basis for the IRS determination.
What Do I Need to Do?
First of all, review the information carefully.
The first-year ACA reporting for 2015 was a particularly difficult one, and one in which the IRS provided extended deadlines and a good faith efforts standard. It is very possible that the numerous challenging systems issues that made the first-year (and, frankly, all subsequent years) ACA reporting so difficult resulted in certain inaccuracies on the 2015 Forms 1094-C and 1095-C.
Be sure to review any potential penalties carefully with your systems records to confirm the reporting was correct.
a) If You Agree with the Penalty Determination – You will complete and return a Form 14764 that is enclosed with the letter, and include full payment for the penalty amount assessed (or pay electronically via EFTPS).
b) If You Disagree with the Penalty Determination – The enclosed Form 14764 will also include a “ESRP Response” form to send to the IRS explaining the basis for your disagreement. You may include any documentation (e.g., employment or offer of coverage records) with the supporting statement.
The response statement will also need to include what changes the ALE would like to make to the Forms 1094-C and/or 1095-C on the enclosed “Employee PTC Listing,” which is a report of the subsidized Exchange enrollment for all of the ALE’s full-time employees. The Letter 226J includes specific instructions on completing this process.
The IRS will respond with a Letter 227 that acknowledges the ALE’s response to Letter 226J and describes any further actions the ALE may need to take. If you disagree with the Letter 227, you can request a “pre-assessment conference” with the IRS Office of Appeals within 30 days from the date of the Letter 227.
If the IRS determines at the end of the correspondence and/or conference that the ALE still owes a penalty, the IRS will issue Notice CP 220J. This is the notice and demand for payment, with a summary of the pay or play penalties due.
Under the Affordable Care Act, (ACA) a fund for a new nonprofit corporation to assist in clinical effectiveness research was created. To aid in the financial support for this endeavor, certain health insurance carriers and health plan sponsors are required to pay fees based on the average number of lives covered by welfare benefits plans. These fees are referred to as either Patient-Centered Outcome Research Institute (PCORI) or Clinical Effectiveness Research (CER) fees.
The applicable fee was $2.26 for plan years ending on or after October 1, 2016 and before October 1, 2017. For plan years ending on or after October 1, 2017 and before October 1, 2018, the fee is $2.39. Indexed each year, the fee amount is determined by the value of national health expenditures. The fee phases out and will not apply to plan years ending after September 30, 2019.
As a reminder, fees are required for all group health plans including Health Reimbursement Arrangements (HRAs), but are not required for health flexible spending accounts (FSAs) that are considered excepted benefits. To be an excepted benefit, health FSA participants must be eligible for their employer’s group health insurance plan and may include employer contributions in addition to employee salary reductions. However, the employer contributions may only be $500 per participant or up to a dollar for dollar match of each participant’s election.
HRAs exempt from other regulations would be subject to the CER fee. For instance, an HRA that only covered retirees would be subject to this fee, but those covering dental or vision expenses only would not be, nor would employee EAPs, disease management programs and wellness programs be required to pay CER fees.
In a recent statement released by the IRS it advised that it would not accept individual 2017 tax returns that did not indicate whether the individual had health coverage, had an exemption from the individual mandate, or will make a shared responsibility payment under the individual mandate. Therefore, for the first time, an individual must complete line 61 (as shown in previous iterations) of the Form 1040 when filing his/her tax return. This article explains what the new IRS position means for the future of ACA compliance from an employer’s perspective.
First, it will be critical (more so this year than in year’s past) that an employer furnish its requisite employees the Form 1095-C by the January 31, 2018 deadline. In previous years, this deadline was extended (to March 2, 2017 last year). However, with the IRS now requiring the ACA information to be furnished by individual tax day, April 17, 2018, employers will almost certainly have to furnish the Form 1095-C to employees by the January 31, 2018 deadline. This is a tight deadline and will require employers to be on top of their data as the 2017 calendar year comes to a close.
An employee who is enrolled in a self-insured plan will need the information furnished in part III of the Form 1095-C to complete line 61 on his/her tax return. It is reasonable to assume that an employee is more likely to inquire as to the whereabouts of the Affordable Care Act information necessary to complete his/her 2017 tax return. Therefore, the possibility of word getting back to the IRS that an employer is not furnishing the Form 1095-C statements to employees is also likely greater in 2017 compared to past years. Remember, an employer can be penalized $260 if it fails to furnish a Form 1095-C that is accurate by January 31, 2018 to the requisite employees. This penalty is capped at $3,218,500. The $260 per Form penalty and the cap amount can be increased if there is intentional disregard for the filing requirements.
The IRS statement continues the IRS’ trend of being more strenuous with ACA requirements. Many employers have received correspondence from the IRS about missing Forms 1094-C and 1095-C for certain EINs. Frequently, this has been caused by the employer incorrectly filing one Form 1094-C for the aggregated ALE group as opposed to a Form 1094-C for each Applicable Large Employer member (ALE member). While the IRS’ latest statement does not ensure that enforcement of the employer mandate (the section 4980H penalties) is coming soon, one could infer that the IRS will soon be sending out penalty notices with respect to the employer mandate.
With the actions taken by the IRS in 2017, all employers need to be taking the reporting of the Forms 1094-C and 1095-C seriously. As of the date of this publication, the Form 1095-C must be furnished to an employer’s requisite employees by January 31, 2018.
The health reform law imposes a number of fees, taxes and other assessments on health insurance companies and sponsors of self-funded health plans to help subsidize a number of endeavors. One such fee funds the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI).
The PCORI fee for calendar year plans is $2.26 per covered life for the 2016 plan year, and must be reported on (and remitted with) IRS Form 720 by July 31, 2017. For non-calendar year plans, if the 2015-16 plan year ended on or before Sept. 30, 2016, the fee is $2.17 per covered life. If the 2015-16 plan year ended between Oct. 1 and Dec. 31, 2016, the fee is $2.26 per covered life. In either case, the filings are similarly due by July 31, 2017. (Note: The Form 720 must be filed by July 31 of the calendar year that begins after the last day of the plan year.)
For self-funded plans, the employer/plan sponsor will be responsible for submitting the fee and accompanying paperwork to the IRS. Third-party reporting and payment of the fee is not permitted for self-funded plans. The process for remitting payment by sponsors of self-funded plans is described in more detail below.
The IRS will collect the fee from the insurer or, in the case of self-funded plans, the plan sponsor/employer in the same way many other excise taxes are collected. IRS regulations provide three options for determining the average number of covered lives (actual count, snapshot and Form 5500 method).
The U.S. Department of Labor believes the fee cannot be paid from plan assets. In other words, the PCORI fee must be paid by the plan sponsor; it is not a permissible expense of a self-funded plan and cannot be paid in whole or part by participant contributions. The IRS has indicated the fee is, however, a tax-deductible business expense for employers with self-funded plans.
The filing and remittance process to the IRS is straightforward and largely unchanged from last year. On page two of Form 720, under Part II, the employer needs to designate the average number of covered lives under its “applicable self-insured plan.” The number of covered lives is multiplied by the applicable amount ($2.26 or $2.17) to determine the total fee owed to the IRS. The Payment Voucher (720-V) should indicate the tax period for the fee is “2nd Quarter.” Failure to properly designate “2nd Quarter” on the voucher will result in the IRS’s software generating a tardy filing notice, with all the incumbent aggravation on the employer to correct the matter with IRS.
With the Republicans’ failure to pass a bill to repeal and replace the Affordable Care Act (ACA), employers should plan to remain compliant with all ACA employee health coverage and annual notification and information reporting obligations.
Even so, advocates for easing the ACA’s financial and administrative burdens on employers are hopeful that at least a few of the reforms they’ve been seeking will resurface in the future, either in narrowly tailored stand-alone legislation or added to a bipartisan measure to stabilize the ACA’s public exchanges. Relief from regulatory agencies could also make life under the ACA less burdensome for employers.
“Looking ahead, lawmakers will likely pursue targeted modifications to the ACA, including some employer provisions,” said Chatrane Birbal, senior advisor for government relations at the Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM). “Stand-alone legislative proposals have been introduced in previous Congresses, and sponsors of those proposals are gearing up to reintroduce bills in the coming weeks.”
These legislative measures, Birbal explained, are most likely to address the areas noted below.
(more…)
Repeal and replacement of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) by the American Health Care Act (AHCA) may be underway in Washington D.C., but until a final version of the AHCA is signed into law, the ACA is the law of the land. In fact, the IRS is currently issuing notices to employers that require them to disclose whether they complied with ACA large employer reporting duties, or their excuse for not doing so, where applicable.
The ACA required large employers to furnish employee statements (Forms 1095-C) and file them with the IRS under transmittal Form 1094-C, and the Internal Revenue Code (“Code”) imposes separate penalty taxes for failing to timely furnish and file the required forms. Large employer reporting was required for 2015 and 2016, even if transition relief from ACA penalty taxes applied for 2015. The potential penalties can be very large – up to $500 per each 2015 Form 1095-C statement ($250 for not furnishing the form to the employee and $250 for not filing it with IRS) – up to a total annual penalty liability of $3 million. The penalty amounts and cap are periodically adjusted for inflation.
Employers that failed to furnish Form 1095-C and file copies with Form 1094-C may receive the IRS notices, called “Request for Employer Reporting of Offers of Health Insurance Coverage (Forms 1094-C and 1095-C)” and also known as Letter 5699 forms. Forms may be received regarding reporting for 2015 or 2016. Employers that receive a Letter 5699 form will have only thirty days to complete and return the form, which contains the following check boxes:
The Letter also provides: “[i]f you are required to file information returns under IRC Section 6056, failure to comply may result in the assessment of a penalty under IRC Section 6721 for a failure to file information returns.”
Employers receiving Letter 5699 forms should contact their benefit advisors immediately and plan to respond as required within the thirty-day limit; it may be necessary to request an extension for employers that are just realizing that they have reporting duties and need to prepare statements for enclosure with their response. In this regard, the IRS offers good faith relief from filing penalties for timely filed but incomplete or incorrect returns for 2015 and 2016, but relief from penalties for failures to file entirely for those years is available only upon a showing of “reasonable cause,” which is narrowly interpreted (for instance, due to fire, flood, or major illness).
Large employers should not look to coming ACA repeal/replacement process for relief from filing duties and potential penalties. The House version of the AHCA does not change large employer reporting duties and it is unlikely the Senate or final versions of the law will do so. This is largely because procedural rules limit reform/repeal provisions to those affecting tax and revenue measures, which would not include reporting rules. Thus the reporting component of the ACA will likely remain intact (though it may be merged into Form W-2 reporting duties), regardless of the ACA’s long-term fate in Washington.
On May 4, 2017, the IRS released Revenue Procedure 2017-37 setting dollar limitations for health savings accounts (HSAs) and high-deductible health plans (HDHPs) for 2018. HSAs are subject to annual aggregate contribution limits (i.e., employee and dependent contributions plus employer contributions). HSA participants age 55 or older can contribute additional catch-up contributions. Additionally, in order for an individual to contribute to an HSA, he or she must be enrolled in a HDHP meeting minimum deductible and maximum out-of-pocket thresholds. The contribution, deductible and out-of-pocket limitations for 2018 are shown in the table below (2017 limits are included for reference).
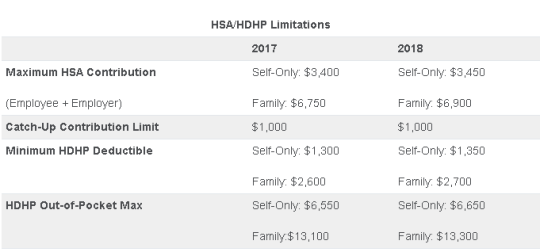
Note that the Affordable Care Act (ACA) also applies an out-of-pocket maximum on expenditures for essential health benefits. However, employers should keep in mind that the HDHP and ACA out-of-pocket maximums differ in a couple of respects. First, ACA out-of-pocket maximums are higher than the maximums for HDHPs. The ACA’s out-of-pocket maximum was identical to the HDHP maximum initially, but the Department of Health and Human Services (which sets the ACA limits) is required to use a different methodology than the IRS (which sets the HSA/HDHP limits) to determine annual inflation increases. That methodology has resulted in a higher out-of-pocket maximum under the ACA. The ACA out-of-pocket limitations for 2018 were announced are are $7350 for single and $14,700 for family.
Second, the ACA requires that the family out-of-pocket maximum include “embedded” self-only maximums on essential health benefits. For example, if an employee is enrolled in family coverage and one member of the family reaches the self-only out-of-pocket maximum on essential health benefits ($7,350 in 2018), that family member cannot incur additional cost-sharing expenses on essential health benefits, even if the family has not collectively reached the family maximum ($14,700 in 2018).
The HDHP rules do not have a similar rule, and therefore, one family member could incur expenses above the HDHP self-only out-of-pocket maximum ($6,650 in 2018). As an example, suppose that one family member incurs expenses of $10,000, $7,350 of which relate to essential health benefits, and no other family member has incurred expenses. That family member has not reached the HDHP maximum ($14,700 in 2018), which applies to all benefits, but has met the self-only embedded ACA maximum ($7,350 in 2018), which applies only to essential health benefits. Therefore, the family member cannot incur additional out-of-pocket expenses related to essential health benefits, but can incur out-of-pocket expenses on non-essential health benefits up to the HDHP family maximum (factoring in expenses incurred by other family members).
Employers should consider these limitations when planning for the 2018 benefit plan year and should review plan communications to ensure that the appropriate limits are reflected.
Yesterday (May 4, 2017) , the House of Representatives narrowly passed the American Health Care Act of 2017 (AHCA), which contains major parts that would repeal and replace the Affordable Care Act (commonly referred to as Obamacare or ACA). The next obstacle the bill faces is making it through the Senate, which proves to be a formidable challenge.
The nonpartisan Congressional Budget Office has not had time yet to analyze the current version of the bill, but this is expected next week. The bill must now pass the Senate and could get pushed back to the House if it sees changes in the upper chamber.
In the meantime, here are some highlights we know about the bill based on how it is written today and how it would work:
We will continue to keep you up to date on the bill as it progress through legislation.