If you employed more than 100 people in the preceding calendar year, you are required to complete and submit your EEOC Report 1 (Survey) by September 30th. You should have received a reminder letter via mail from the EEOC in August also with the link to file the report online.
Please contact our office for information about the EEOC Report 1 or for the link to the EEOC’s web based filing system.
Courtesy of Fisher & Phillips LLP
The Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) recently rolled out a pilot program to electronically notify employers of new charges filed against them. Instead of mailing the Notice of Charge of Discrimination form through conventional means, the EEOC is rolling out a new system that will notify an employer of a pending charge and allow an employer to respond to the charge through an online portal.
This new system is catching a lot of employers by surprise, and has resulted in many questions. Fisher & Phillips has developed a list of Frequently Asked Questions to aid employers in understanding this new pilot program.
What is this new system?
The EEOC is piloting a new electronic system involving an online portal called
ACT Digital. If a new Charge of Discrimination is filed against you, the EEOC
will email you notice of the new Charge and invite you to download a copy
through the portal.
Phase I of the project only allows employers a channel of communication with the EEOC about the Charge. Charging Parties are not yet allowed electronic access. In this first phase, upon consenting to certain terms and conditions, you are able to:
The EEOC has indicated that employers will also be able to use ACT Digital to communicate with the EEOC regarding extensions, inquiries, and other Charge-related issues. It seems this option may already be operational in some EEOC offices.
Where is the EEOC implementing ACT Digital?
The EEOC is rolling out ACT Digital in waves. The first wave began in early May
2015 and included EEOC offices in San Francisco and Charlotte. Earlier this
summer, the EEOC released the program in a second wave of offices, which
included Denver, Detroit, Indianapolis, and Phoenix. The EEOC’s goal is to
implement ACT Digital in all of its 53 offices by October 2015.
How will we first receive notice?
The EEOC will send an email containing a Charge notification to an employer’s
representative. The EEOC might obtain this email address from the Charging Party,
or may obtain it from past email communications with those businesses already
in the EEOC’s system.
Note that this could result in a manager or supervisor receiving notice of a Charge outside his or her own department or area. We are still checking to see if the EEOC will allow employers to proactively designate an email address where all notices to the company should be sent.
Must employers use this system?
This is the most common question we’ve received so far. The short answer is no
– for now. Employers are currently not required to use ACT
Digital during the pilot period of implementation. Note that if you do respond
to the initial email, you may be creating an obligation to use the system going
forward, thereby limiting your position with regard to how the Charge is
handled.
However, the EEOC is transitioning to an entirely electronic format and, as a practical matter, all employers will likely be required to use this electronic system in the future.
What if the notification email is blocked by a
firewall or spam folder?
The EEOC’s notification procedure includes some “fail-safes” to ensure you do
not miss notifications of pending Charges. For example, the EEOC may send a
hard copy of the Charge if the online portal is not accessed by the employer
within approximately 10 days after the notice email is sent.
Can the Charge be viewed by the public?
No, with one exception. Each Charge has a unique portal access that you will
use for the life of the case. Therefore, only people with access through the
unique portal address will be able to access ACT Digital to view the Charge and
your Position Statement. At this time, even the Charging Party does not have
access to the online portal.
The one exception – which has always been the case – is that the public may request Charge files under the Freedom of Information Act (FOIA). The EEOC has stated that it will continue to follow its current protocols and federal regulations in responding to FOIA requests (which typically do not allow for access to the Charge while the matter is pending).
Similarly, the unique portals will close after a period of time. We do not know for sure, but it is believed the portals will be deactivated 90 to 100 days after the EEOC closes the file. Because the portals expire, you should download and retain all necessary files and documents related to the Charge if they use the electronic system.
Will state human affairs commissions use ACT
Digital?
At this time, the EEOC has not indicated whether state human affairs
commissions will be utilizing the ACT Digital system.
What will Phase II look like?
The EEOC has released very little information about Phase II and any
speculation as to what is in the pipeline is just that – speculation. With that
caveat, there are a few likely next moves.
We expect the EEOC will open the portal to Charging Parties so they may file and monitor their Charges online. It is unknown, however, whether the portals will be kept separate or combined. In the future, the EEOC may also maintain a database of the employer’s prior Charges, as opposed to deactivating the portal.
What should we do immediately?
Because you could receive notice of a new Charge tomorrow, you should instruct
all of your supervisors and managers today to immediately contact the HR
department or in-house counsel if they get an email from the EEOC. Just as in
the past you instructed them to forward on any hard copy EEOC Charge received
in the mail, the same rule should apply for electronic notices.
You should take it one step further in this digital age: counsel your managers not only to forward on EEOC emails to proper company channels without responding, but also to refrain from downloading the Charge or even clicking anywhere on the email.
Phase I of the ACT Digital rollout should not drastically affect how you respond to EEOC Charges. In fact, it might make communication with the EEOC easier. As additional phases are rolled out, however, this could change. Stay tuned for more updates.
Do you want to learn more?
Fisher & Phillips LLP is hosting a free, 20-minute webinar on this subject on Thursday, September 10, 2015, at 12:00pm EST. You can register for “EEOC Goes Electronic: FAQs On EEOC’s New Electronic Pilot Program” by visiting their website (www.laborlawyers.com) and looking under the “Events” tab.
In July 2015, President Obama signed into law the Trade Preferences Extension Act of 2015. Included in the bill was an important provision that affects welfare and retirement benefit plans. The Act sizably increases filing penalties for information return and statement failures under the Internal Revenue Code, effective for filings after December 31,2015. Employers now face significantly larger penalties for failing to correctly file and furnish the ACA forms 1094 and 1095 (shared responsibility reporting requirements) as well as Forms W-2 and 1099-R.
Background
Sections 6721 and 6722 of the IRC impose penalties associated with failures to file- or to file correct- information returns and statements. Section 6721 applies to the returns required to be filed with the IRS, and Section 6722 applies to statements required to be provided generally to employees.These penalty provisions apply to the ACA shared responsibility reporting Forms 1094-B, 1094-C, 1095-B, and 1095-C (Sections 6055 & 6056) failures as well as other information returns and statement failures, like those on Forms W-2 and 1099.
For ACA:
The Sections 6055 & 6056 reporting requirements are effective for medical coverage provided on or after January 1, 2015, with the first information returns to be filed with the IRS by February 29, 2016 (or March 31,2016 if filing electronically) and provided to individuals by February 1, 2016.
Increase in Penalties
The Trade Preferences Extension Act of 2015 (Act) contains several tax provisions in addition to the trade measures that were the focus of the bill. Provided as a revenue offset provision, the law significantly increases the penalty amounts under Sections 6721 and 6722. A failure includes failing to file or furnish information returns or statements by the due date, failing to provide all required information, as well as failing to provide correct information.
The law increases the penalty for:
Other penalty increase also apply, including those associated with timely filing a corrected return. Penalties could also provide a one-two punch under the ACA for employers and other responsible entities. For example, under Sec 6056, applicable large employers (ALE) must file information returns to the IRS (the 1094-B and 1094-C) as well as furnish statements to employees (the 1095-B and 1095-C). So incorrect information shared on those forms could result in a double penalty- one associated with the information return to the IRS and the other associated with individual statements to employees.
Final regulations on the ACA reporting requirements provide short-term relief from these penalties. For reports files in 2016 (for 2015 calendar year info), the IRS will not impose penalties on ALE members that can show they made a “good-faith effort” to comply with the information reporting requirements. Specifically, relief is provided for incorrect or incomplete info reported on the return or statement, including Social Security numbers, but not for failing to file timely.
Failure to thoroughly complete I-9 paperwork has left an event-planning company with a fine of $605,250 (the largest amount ever ordered) serving as a reminder that employers need to be taking I-9 compliance very seriously.
On July 8, 2015, the Office of the Chief Administrative Hearing Officer (OCAHO), which has jurisdiction to review civil penalties for I-9 violations, ordered Hartmann Studios to pay the fine for more than 800 I-9 paperwork violations.
Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) audited the company in March 2011.
The bulk of the violations charged against Hartmann were due to a repeated failure to sign section 2 of the I-9 form. Employers are required to complete and sign section 2 within three business days of a hire, attesting under penalty of perjury that the appropriate verification and employment authorization documents have been reviewed.
ICE found 797 I-9s where section 2 was incomplete. About half of these incomplete forms related to individuals from the International Alliance of Theatrical Stage Employees Union Local 16A, who worked for Hartmann on a project-by-project basis during the term of a collective bargaining agreement. Even though the union workers worked on a project-by-project basis, they were not terminated upon completion of a project and remained “on-call.” The union created a “three-in-one” form that combined a portion of a W-4 form, parts of sections 1 and 2 of an I-9 form, and a withholding authorization for union dues. No separate I-9 form was completed for these workers nor did Hartmann sign section 2 of the union form.
Hartmann could have been charged with the more-substantive offense of having failed to prepare any I-9 form at all for the 399 union members, because the union’s form is not compliant, but OCAHO declined to do so.
Hartmann told OCAHO it believed that the union form was sufficient to confirm that the workers had proper employment authorization, and that nothing further needed to be done to confirm their eligibility for employment. The company also said that it did not know signing section 2 of the form was a legal requirement.
In addition to failing to sign section 2, Hartmann was also cited for:
This case demonstrates the need for employers to conduct routine self-audits of their I-9 inventories to ensure that the forms have been properly completed and retained and are ready for inspection.
Employers should also ensure that acceptable proof of audits and training is kept so that it may be used as evidence of good faith in court proceedings.
After more than 15 months of waiting, the U.S. Department of Labor has issued a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking (“NPRM”) announcing the Department’s intention to shrink dramatically the pool of employees who qualify for exempt status under the Fair Labor Standards Act.
The 295-page NPRM, released June 30, contains a few specific changes to existing DOL regulations: more than doubling the salary threshold for the executive, administrative, and professional exemptions from $455 a week currently to $921 a week (with a plan to increase that number to $970 a week in the final version of the regulation), as well as raising the pay thresholds for certain other exemptions, and building in room for future annual increases. More ominously, the Department invites comment on a host of other issues. This opens the door to many further significant revisions to the regulations in a Final Rule after the Department reviews the public’s comments to the NPRM.
Background
On March 13, 2014, President Obama directed the Secretary of Labor to modernize and streamline the existing overtime regulations for exempt executive, administrative, and professional employees. He said the compensation paid to these employees has not kept pace with America’s economy since the Department last revised regulations in 2004. The President noted that the minimum annual salary level for these exempt classifications under the 2004 regulations is $23,660, which is below the poverty line for a family of four.
Since the President issued his memo, the Department has held meetings with a variety of stakeholders, including employers, workers, trade associations, and other advocates. The Department has raised questions about how the current regulations work and how they can be improved. The discussions have focused on the compensation levels for the exempt classifications as well as the duties required to qualify for exempt status.
The NPRM
The NPRM expressed the Department’s intention to increase the salary threshold for the white-collar exemptions from $455 a week (or $23,660 a year) to $921 a week ($47,892 a year), which the Department expects to revise to $970 a week ($50,440 a year in 2016) when it issues its Final Rule. Under this single change to the regulations, it is estimated that 4.6 million currently exempt employees would lose their exemption right away, with another 500,000 to 1 million currently exempt employees losing exempt status over the next 10 years as a result of the automatic increases to the salary threshold.
The NPRM acknowledges that roughly 25% of all employees currently exempt and subject to the salary basis requirement will be rendered non-exempt under the proposed regs. The Department recognizes that employers are likely to reduce the working hours of currently exempt employees reclassified as a result of these regulations, and that the reduction in hours will probably lead to lower overall pay for these employees.
Related changes in the regs include increasing the annual compensation threshold for exempt highly compensated employees from the present level of $100,000 to a proposed $122,148, as well as raising the exemption threshold for the motion picture producing industry from the present $695 a week to a proposed $1,404 a week for employees compensated on a day-rate basis.
Perhaps not surprisingly, given the likely impact of the proposal, almost all of the NPRM is devoted to economic analysis and justification for the steep increase in the salary thresholds. Nevertheless, the NPRM touches on some other topics as well. The Department states that it is considering, and invites comment on, a wide range of topics, including:
What Comes Next?
The proposed regulations are subject to a 30-day public comment period. Now is the time for any employer or trade association dissatisfied with the proposed regulatory text, or concerned about changes the Department is weighing for inclusion in a Final Rule, to submit comments. The Department has put the regulated public on notice: it is considering sweeping changes to the regulations not described specifically in the proposed regulatory text, such as altering the duties tests for exempt status. Employers may not have another opportunity to comment on the content of a Final Rule.
Following the public comment period, the Department will issue a Final Rule that may add, change, delete, or affirm the regulatory text of the proposal. The Office of Management and Budget will review the Final Rule before publication. This process is likely to take at least six to eight months. A Final Rule is not expected before 2016.
The Supreme Court left one of its most high-profile decisions for the end of its term, holding today by a 5-4 vote that the Constitution requires states to recognize same-sex marriage. As a result, state bans against same-sex marriage are no longer permissible and all states are required to recognize same-sex marriages that take place in other states. Employers should update their FMLA policies and benefit plans to provide the same coverage for same-sex married couples as for other married couples. Obergefell v. Hodges.
Background
In 2013, the U.S. Supreme Court ruled that Section 3 of the Federal Defense of
Marriage Act (DOMA), which essentially barred same-sex married couples from
being recognized as “spouses” for purposes of federal laws, violated the Fifth
Amendment (United States v.
Windsor). On the heels of that case, same-sex couples sued their
relevant state agencies in Ohio, Michigan, Kentucky, and Tennessee to challenge
the constitutionality of those states’ same-sex marriage bans, as well as their
refusal to recognize legal same-sex marriages that occurred in other
jurisdictions.
For instance, the named plaintiff, James Obergefell, married a man named John Arthur in Maryland. Arthur died a few months later in Ohio where the couple lived, but Obergefell did not appear on his death certificate as his “spouse” because Ohio does not recognize same-sex marriage. Similarly, Army Reserve Sergeant First Class Ijpe DeKoe married Thomas Kostura in New York, which permits same-sex marriage. When Sgt. DeKoe returned from Afghanistan, the couple moved to Tennessee, but that state refused to recognize their marriage.
The plaintiffs in each case argued that the states’ refusal to recognize their same-sex marriages violated the Equal Protection Clause and Due Process Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment. In all the cases, the trial court found in favor of the plaintiffs. The U.S. Court of Appeals for the Sixth Circuit reversed and held that states’ bans on same-sex marriage and refusal to recognize marriages performed in other states did not violate Fourteenth Amendment rights to equal protection and due process.
The Supreme Court accepted review of the controversy, focusing its analysis on whether the Constitution requires all states to recognize same-sex marriage, and whether it requires a state which refuses to recognize same-sex marriage to nevertheless recognize same-sex marriages entered into in other states where such unions are permitted.
Same-Sex
Marriage Is Guaranteed By The Constitution
In its ruling today, the Supreme Court sided with the plaintiffs and held that
marriage is a fundamental right; as such, same-sex couples cannot be deprived
of that right pursuant to the Due Process and Equal Protection Clauses of the
Fourteenth Amendment.
Practical
Impact On Employers: FMLA Policies and Benefit Documents Must Be Updated
Following Windsor, the Department of
Labor issued a Final Rule revising FMLA’s definition of “spouse” to ensure that
same-sex married couples receive FMLA rights and protections without regard to
where they reside. Specifically, the DOL’s Final Rule adopts a “place of
celebration” rule, meaning that when defining a spouse under the FMLA, it
refers “to the other person with whom an individual entered into marriage as
defined or recognized under state law for purposes of marriage in the State in
which the marriage was entered into or, in the case of a marriage entered into
outside of any State, if the marriage is valid in the place where entered into
and could have been entered into in at least one State.” In other words, this
broad interpretation was intended to ensure that FMLA coverage existed for
same-sex couples even in states where same-sex marriage was banned.
The Final Rule had been temporarily enjoined in Texas, Arkansas, Louisiana, and Nebraska by a federal judge who ruled that the DOL did not have the authority to change the definition of “spouse,” and that the change “improperly preempts state law forbidding the recognition of same-sex marriages for the purpose of state-given benefits.” That litigation was on hold pending the outcome of this case. The Supreme Court’s decision in Obergefell paves the way for the Final Rule to go into effect, which means that employers should update their FMLA policies accordingly.
Additionally, employers should review their benefit offerings and consider the impact this decision has on employees who are in same-sex marriages.
Ironically, the Obergefell decision does not change the fact that sexual orientation is still not a protected class under federal law for employment law purposes. Although many states and municipalities protect against discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation, the proposed amendment to Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 remains in limbo.
In a 6-3 decision handed down June 25th by the U.S. Supreme Court, the IRS was authorized to issue regulations extending health insurance subsidies to coverage purchased through health insurance exchanges run by the federal government or a state (King v. Burwell, No. 14-114 ).
This means employers cannot avoid employer shared responsibility penalties under IRC section 4980H (“Code § 4980H”) with respect to an employee solely because the employee obtained subsidized exchange coverage in a state that has a health insurance exchange set up by the federal government instead of by the state. It also means that President Barack Obama’s 2010 health care reform law will not be unraveled by the Supreme Court’s decision in this case. The law’s requirements applicable to employers and group health plans continue to apply without change.
What Was the Case About?
IRC section 36B (“Code § 36B”), created by the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act of 2010 (“ACA”), provides that an individual who buys health insurance “through an Exchange established by the State under section 1311 of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act” (emphasis added) generally is entitled to subsidies unless the individual’s income is too high. Thus, the words of the statute conditioned one’s right to an exchange subsidy on one’s purchase of ACA coverage in a state run exchange.
Since 2014, an individual who fails to maintain health insurance for any month generally is subject to a tax penalty unless the individual can show that no affordable coverage was available. The law defines affordability for this purpose in such a way that, without a subsidy, health insurance would be unaffordable for most people.
The plaintiffs in King, residents of one of the 34 states that did not establish a state run health insurance exchange argued that if subsidies were not available to them, no health insurance coverage would be affordable for them and they would not be required to pay a penalty for failing to maintain health insurance. The IRS, however, made subsidized federal exchange coverage available to them similar to coverage in a state run exchange.
It is ACA § 1311 that established the funding and other incentives for “the States” to each establish a state-run exchange through which residents of the state could buy health insurance. Section 1311 also provides that the Secretary of the Treasury will appropriate funds to “make available to each State” and that the “State shall use amounts awarded for activities (including planning activities) related to establishing an American Health Benefit Exchange.” Section 1311 describes an “American Health Benefit Exchange” as follows:
Each State shall, not later than January 1, 2014, establish an American Health Benefit Exchange (referred to in this title as an “Exchange”) for the State that (A) facilitates the purchase of qualified health plans; (B) provides for the establishment of a Small Business Health Options Program and © meets [specific requirements enumerated].
An entirely separate section of the ACA provides for the establishment of a federally-run exchange for individuals to buy health insurance if they reside in a state that does not establish a 1311 exchange. That section – ACA § 1321 – withholds funding from a state that has failed to establish a 1311 exchange.
Notwithstanding the statutory language Congress used in the ACA (i.e., literally conditioning an individual’s eligibility subsidized exchange coverage on the purchase of health insurance through a state’s 1311 exchange), the Supreme Court determined that the language is ambiguous. Having found that the text is ambiguous, the Court stated that it must determine what Congress really meant by considering the language in context and with a view to the placement of the words in the overall statutory scheme.
When viewed in this context, the Court concluded that the plain language could not be what Congress actually meant, as such interpretation would destabilize the individual insurance market in those states with a federal exchange and likely create the “death spirals” the ACA was designed to avoid. The Court reasoned that Congress could not have intended to delegate to the IRS the authority to determine whether subsidies would be available only on state run exchanges because the issue is of such deep economic and political significance. The Court further noted that “had Congress wished to assign that question to an agency, it surely would have done so expressly” and “[i]t is especially unlikely that Congress would have delegated this decision to the IRS, which has no expertise in crafting health insurance policy of this sort.”
What Now?
Regardless of whether one agrees with the Supreme Court’s King decision, the decision prevents any practical purpose for further discussion about whether the IRS had authority to extend taxpayer subsidies to individuals who buy health insurance coverage on federal exchanges.
The ACA’s next major compliance requirements for employers: Employers with fifty or more fulltime and fulltime equivalent employees need to ensure that they are tracking hours of service and are otherwise prepared to meet the large employer reporting requirements for 2015 (due in early 2016) ). Employers of any size that sponsor self-funded group health plans need to ensure that they are prepared to meet the health plan reporting requirements for 2015 (also due in early 2016). All employers that sponsor group health plans also should be considering whether and to what extent the so-called Cadillac tax could apply beginning in 2018.
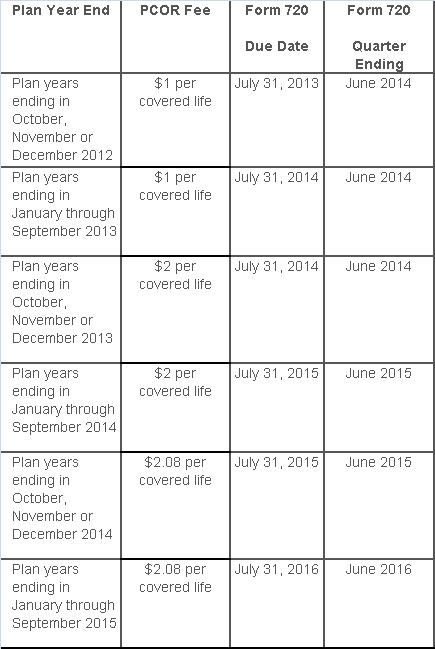
The Affordable Care Act added a patient-centered outcomes research (PCOR) fee on health plans to support clinical effectiveness research. The PCOR fee applies to plan years ending on or after Oct. 1, 2012, and before Oct. 1, 2019. The PCOR fee is due by July 31 of the calendar year following the close of the plan year. For plan years ending in 2014, the fee is due by July 31, 2015.
PCOR fees are required to be reported annually on Form 720, Quarterly Federal Excise Tax Return, for the second quarter of the calendar year. The due date of the return is July 31. Plan sponsors and insurers subject to PCOR fees but not other types of excise taxes should file Form 720 only for the second quarter, and no filings are needed for the other quarters. The PCOR fee can be paid electronically or mailed to the IRS with the Form 720 using a Form 720-V payment voucher for the second quarter. According to the IRS, the fee is tax-deductible as a business expense.
The PCOR fee is assessed based on the number of employees, spouses and dependents that are covered by the plan. The fee is $1 per covered life for plan years ending before Oct. 1, 2013, and $2 per covered life thereafter, subject to adjustment by the government. For plan years ending between Oct. 1, 2014, and Sept. 30, 2015, the fee is $2.08. The Form 720 instructions are expected to be updated soon to reflect this increased fee.
This chart summarizes the fee schedule based on the plan year end and shows the Form 720 due date. It also contains the quarter ending date that should be reported on the first page of the Form 720 (month and year only per IRS instructions). The plan year end date is not reported on the Form 720.
For insured plans, the insurance company is responsible for filing Form 720 and paying the PCOR fee. Therefore, employers with only fully- insured health plans have no filing requirement.
If an employer sponsors a self-insured health plan, the employer must file Form 720 and pay the PCOR fee. For self-insured plans with multiple employers, the named plan sponsor is generally required to file Form 720. A self-insured health plan is any plan providing accident or health coverage if any portion of such coverage is provided other than through an insurance policy.
Since the fee is a tax assessed against the plan sponsor and not the plan, most funded plans subject to ERISA must not pay the fee using plan assets since doing so would be considered a prohibited transaction by the U.S. Department of Labor (DOL). The DOL has provided some limited exceptions to this rule for plans with multiple employers if the plan sponsor exists solely for the purpose of sponsoring and administering the plan and has no source of funding independent of plan assets.
Plans sponsored by all types of employers, including tax-exempt organizations and governmental entities, are subject to the PCOR fee. Most health plans, including major medical plans, prescription drug plans and retiree-only plans, are subject to the PCOR fee, regardless of the number of plan participants. The special rules that apply to Health Reimbursement Accounts (HRAs) and Health Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs) are discussed below.
Plans exempt from the fee include:
If a plan sponsor maintains more than one self-insured plan, the plans can be treated as a single plan if they have the same plan year. For example, if an employer has a self-insured medical plan and a separate self-insured prescription drug plan with the same plan year, each employee, spouse and dependent covered under both plans is only counted once for purposes of the PCOR fee.
The IRS has created a helpful chart showing how the PCOR fee applies to common types of health plans.
Health Reimbursement Accounts (HRAs) - Nearly all HRAs are subject to the PCOR fee because they do not meet the conditions for exemption. An HRA will be exempt from the PCOR fee if it provides benefits only for dental or vision expenses, or it meets the following three conditions:
Health Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs) - A health FSA is exempt from the PCOR fee if it satisfies an availability condition and a maximum benefit condition.
Additional special rules for HRAs and FSAs . Once an employer determines that its HRA or FSA is subject to the PCOR fee, the employer should consider the following special rules:
The IRS provides different rules for determining the average number of covered lives (i.e., employees, spouses and dependents) under insured plans versus self-insured plans. The same method must be used consistently for the duration of any policy or plan year. However, the insurer or sponsor is not required to use the same method from one year to the next.
A plan sponsor of a self-insured plan may use any of the following three
methods to determine the number of covered lives for a plan year:
1. Actual count method. Count the covered lives on each day of the plan year and divide by the number of days in the plan year.
Example: An employer has 900 covered lives on Jan. 1, 901 on Jan. 2, 890 on
Jan. 3, etc., and the sum of the lives covered under the plan on each day of
the plan year is 328,500. The average number of covered lives is 900 (328,500 ÷
365 days).
2. Snapshot method. Count the covered lives on a single day in each quarter (or more than one day) and divide the total by the number of dates on which a count was made. The date or dates must be consistent for each quarter. For example, if the last day of the first quarter is chosen, then the last day of the second, third and fourth quarters should be used as well.
Example: An employer has 900 covered lives on Jan. 15, 910 on April 15, 890 on
July 15, and 880 on Oct. 15. The average number of covered lives is 895 [(900 +
910+ 890+ 880) ÷ 4 days].
As an alternative to counting actual lives, an employer can count the number of
employees with self-only coverage on the designated dates, plus the number of
employees with other than self-only coverage multiplied by 2.35.
3. Form 5500 method. If a Form 5500 for a plan is filed before the due date of the Form 720 for that year, the plan sponsor can determine the number of covered lives based on the Form 5500. If the plan offers just self-only coverage, the plan sponsor adds the participant counts at the beginning and end of the year (lines 5 and 6d on Form 5500) and divides by 2. If the plan also offers family or dependent coverage, the plan sponsor adds the participant counts at the beginning and end of the year (lines 5 and 6d on Form 5500) without dividing by 2.
Example: An employer offers single and family coverage with a plan year ending
on Dec. 31. The 2013 Form 5500 is filed on June 5, 2014, and reports 132
participants on line 5 and 148 participants on line 6d. The number of covered
lives is 280 (132 + 148).
To evaluate liability for PCOR fees, plan sponsors should identify all of their plans that provide medical benefits and determine if each plan is insured or self-insured. If any plan is self-insured, the plan sponsor should take the following actions:
While the rest of us were enjoying our Memorial Day holiday, the Department of Labor was busy posting the new model FMLA notices and medical certification forms… with an expiration date of May 31, 2018!
No more month-to-month extensions or lost sleep over when the long-awaited forms would be released.
That said, it couldn’t have taken DOL a whole lot of time to draft the updated forms. After a relatively close review of the new forms, the notable change is a reference to the Genetic Information Nondiscrimination Act (GINA). In the instructions to the health care provider on the certification for an employee’s serious health condition, the DOL has added the following simple instruction:
Do not provide information about genetic tests, as defined in 29 C.F.R. § 1635.3(f), genetic services, as defined in 29 C.F.R. § 1635.3(e), or the manifestation of disease or disorder in the employee’s family members, 29 C.F.R. § 1635.3(b).
The DOL added similar language to the other medical certification forms as well. For years, employers have included GINA disclaimers in their FMLA paperwork, and those disclaimers typically have been far more robust (and reader-friendly) than the cryptic one the DOL used above.
For easy reference, here are the links to the new FMLA forms:
The forms also can be accessed from this DOL web page.
According to recent news reports, nearly half of the 17 Exchanges run by states and the District of Columbia under the Affordable Care Act (ACA) are struggling financially:
Many of the online exchanges are wrestling with surging costs, especially for balky technology and expensive customer call centers — and tepid enrollment numbers. To ease the fiscal distress, officials are considering raising fees on insurers, sharing costs with other states and pressing state lawmakers for cash infusions. Some are weighing turning over part or all of their troubled marketplaces to the federal exchange, HealthCare.gov, which now works smoothly.
Of course, many states can’t solve their financial troubles easily. As independent entities, their income depends on fees imposed on insurers, which is then often passed on to the consumer signing up for health care. However, those fees are entirely contingent on how many people enroll in that particular Exchange; low enrollment invariably means higher costs.
Low enrollment is where the trouble thickens. The recently completed open enrollment period only rose 12 percent to 2.8 million sign-ups for state Exchanges, according to The Washington Post. Comparatively, the federal Exchange saw an increase of 61 percent to 8.8 million people.
According to the Post, state Exchanges have operating budgets between “$28 million and $32 million”. Most of the money tends to go to call centers, “Enrollment can be a lengthy process — and in several states, contractors are paid by the minute. An even bigger cost involves IT work to correct defective software that might, for example, make mistakes in calculating subsidies.”
However, The Fiscal Times contends that, “Some states may be misusing Obamacare grants in order to keep their state insurance exchanges operating—potentially flouting a provision in the law requiring them to cover the costs of the exchanges themselves starting this year.”
In fact, the ACA provided about $4.8 billion in grants to help states build and promote their Exchanges. As the article explains, before this year, states could use the grant money on overhead costs. However, a new provision that went into effect in January 2015 says that states can’t use the grants on maintenance and staffing costs; grant money must be spent on design, development and implementation costs.
The Fiscal Times spotlights California as a prime example of why state Exchanges are in troubled waters:
One of the worst examples comes from California, where the state’s exchange has been touted the most successful in the country for enrolling thousands of people. Covered California has already used up about $1.1 billion in federal funding to get its exchange up and running and is now expected to run a nearly $80 million deficit by the end of the year, according to the Orange County Register. The state has already set aside about $200 million to cover that, but the long-term sustainability of the program is very much in question.
In addition, state Exchanges like Hawaii might have to switch to the federal Exchange, Healthcare.gov, because of on-going financial solvency issues. “This is a contingency that is being imposed on any state-based exchange that doesn’t have a funded sustainability plan in play,” said Jeff Kissel, CEO of the Hawaii Health Connector.
According to the Post, states with the lowest enrollment are facing the biggest financial problems:
Turning operations over to the federal Exchange seems to be a popular alternative, but it doesn’t come without a cost: $10 million per Exchange, to be exact.
Although there are many options for state Exchanges to consider, it is likely that they will hold off on any final decisions until after the Supreme Court decides King v. Burwell. In this case, the Chief Justices will make a ruling in June that could either send a lifeline to ACA or remove a fundamental pillar of the law by under-cutting its ability to extend health insurance coverage to millions of Americans through its subsidy program.
The appellants in the King v. Burwell case say that IRS rule conflicts with the statutory language set forth in the ACA, which limits subsidy payments to individuals or families that enroll in the state-based Exchanges only. If the Court relies on a literal interpretation of the ACA’s language, millions of Americans who live in more than half of the states where the federal Exchange operates will not receive subsidies, thus undoing a fundamental pillar of the law. (Read more about the court case here.)